Handle Multiple Windows
Handling multiple windows in Selenium involves managing different browser windows or tabs that are opened during a test session. Selenium WebDriver provides mechanisms to switch between these windows, allowing interactions in each one. Here’s a comprehensive guide on how to handle multiple windows in Selenium:
Key Concepts
1. Window Handle:
- A window handle is a unique identifier assigned to each browser window or tab.
- Selenium uses these handles to switch between different windows.
2. Switching Windows:
driver.switchTo().window(windowHandle):
Common Steps in Handling Multiple Windows:
1. Identify and Store Window Handles:
driver.getWindowHandles()
2. Switching Context:
- Once you have the window handles, you can use
driver.switchTo().window(windowHandle)
to switch the WebDriver’s context to the desired window or tab.
3. Perform Actions:
- After switching to a particular window, you can interact with the elements in that window (e.g., fill out forms, click buttons).
4. Switching Back:
- You may need to switch back to the original window or move to another window as your test requires.
Coding of handling Multiple Windows
package asc;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.Set;
import org.openqa.selenium.By;
import org.openqa.selenium.chrome.ChromeDriver;
import io.github.bonigarcia.wdm.WebDriverManager;
public class MultipleWindows {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
WebDriverManager.chromedriver().setup();
ChromeDriver driver = new ChromeDriver();
driver.get("https://www.salesforce.com/in/?ir=1");
driver.manage().window().maximize();
driver.findElement(By.xpath("//*[@id=\"1682325589592_4ma\"]/div[1]/article/div[2]/div/pbc-button[1]")).click();
Thread.sleep(4000);
Set windowhandles = driver.getWindowHandles();
System.out.println(windowhandles);
Iterator iterator = windowhandles.iterator();
String parentwindow = iterator.next();
System.out.println(parentwindow);
String childwindow = iterator.next();
System.out.println(childwindow);
driver.switchTo().window(childwindow);
Thread.sleep(4000);
driver.findElement(By.name("UserFirstName")).sendKeys("Akhil");
Thread.sleep(4000);
driver.findElement(By.name("UserLastName")).sendKeys("Chukkalwar");
driver.switchTo().window(parentwindow);
}
}

Output
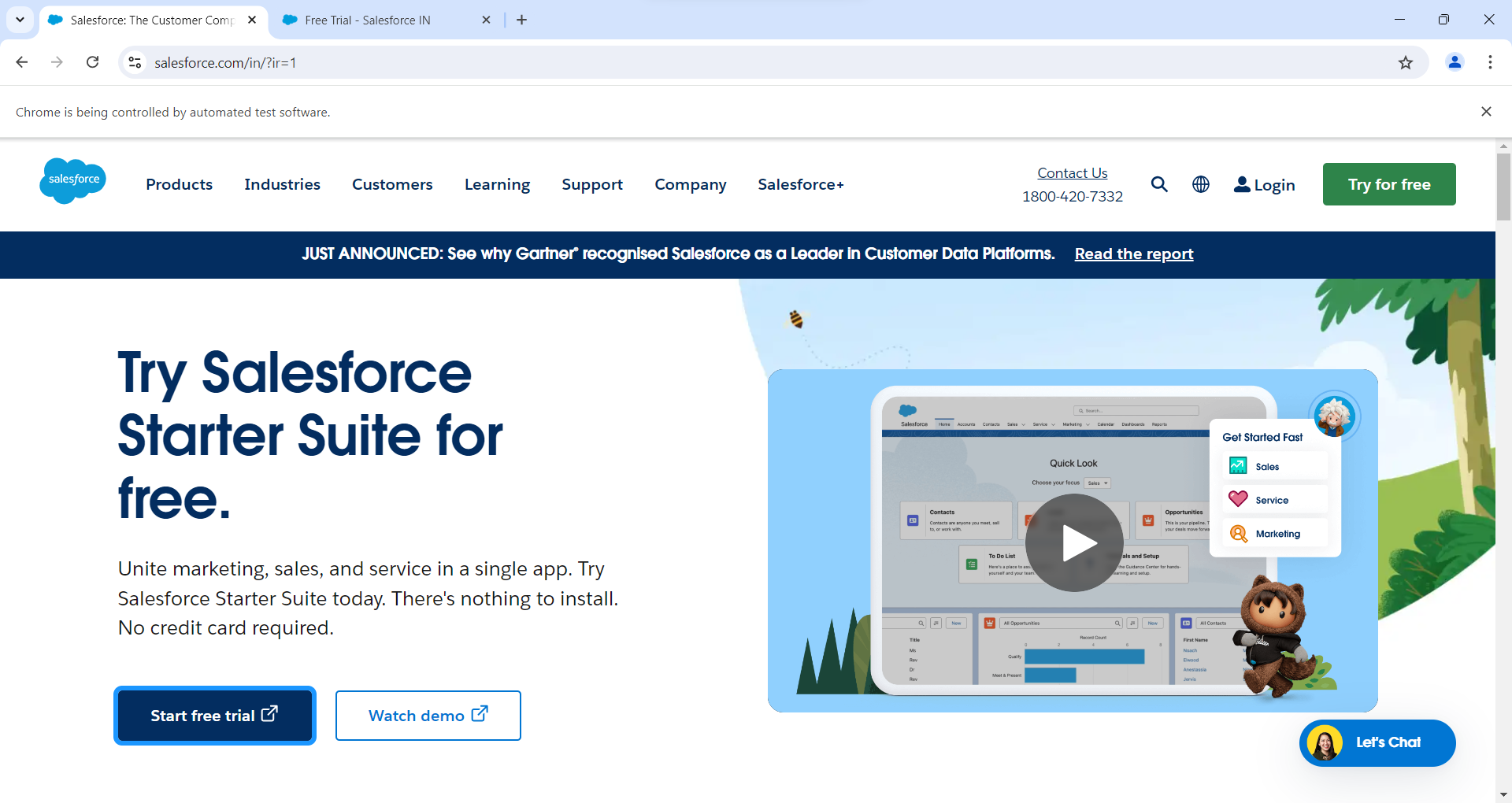
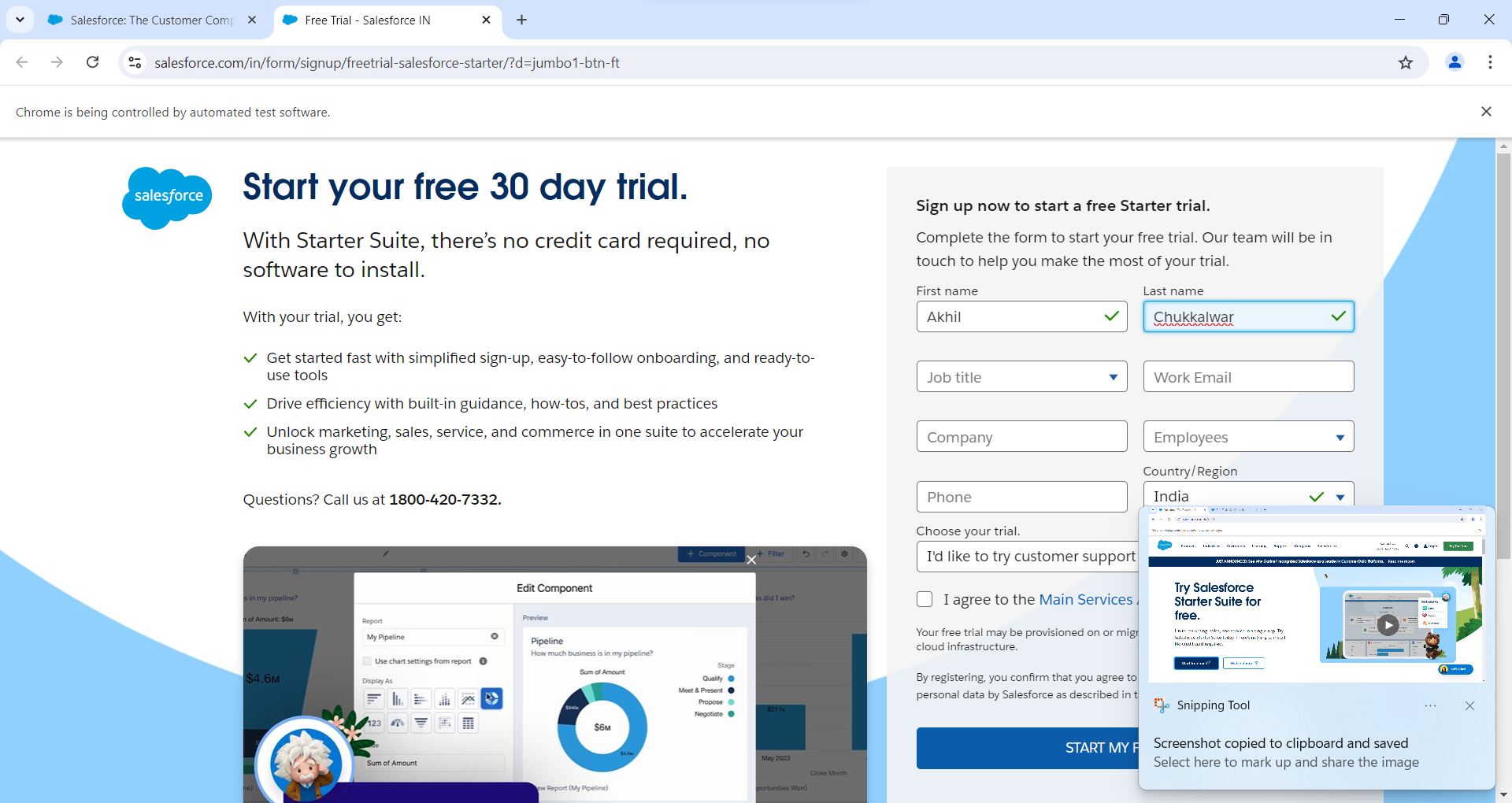

Code Breakdown and Explanation:
1. Setup and Navigation:
WebDriverManager.chromedriver().setup();
ChromeDriver driver = new ChromeDriver();
driver.get("https://www.salesforce.com/in/?ir=1");
driver.manage().window().maximize();
WebDriverManager.chromedriver().setup();
new ChromeDriver();
driver.get(...);
driver.manage().window().maximize();
2. Interacting with the Page:
driver.findElement(By.xpath("//*[@id=\"1682325589592_4ma\"]/div[1]/article/div[2]/div/pbc-button[1]")).click();
3. Handling Multiple Windows:
Thread.sleep(4000); Setwindowhandles = driver.getWindowHandles(); System.out.println(windowhandles);
Thread.sleep(4000);
driver.getWindowHandles();
System.out.println(windowhandles);
4. Switching Between Windows:
Iterator iterator = windowhandles.iterator();
String parentwindow = iterator.next();
System.out.println(parentwindow);
String childwindow = iterator.next();
System.out.println(childwindow);
driver.switchTo().window(childwindow);
Iteratoriterator = windowhandles.iterator();
String parentwindow = iterator.next();
String childwindow = iterator.next();
driver.switchTo().window(childwindow);
5. Interacting with Elements in the New Window:
Thread.sleep(4000);
driver.findElement(By.name("UserFirstName")).sendKeys("Akhil");
Thread.sleep(4000);
driver.findElement(By.name("UserLastName")).sendKeys("Chukkalwar");
6. Switching Back to the Original Window:
driver.switchTo().window(parentwindow);
Key Points
- Window Handles: Each window or tab opened by the WebDriver has a unique handle. These handles are used to switch between different windows or tabs.
- Switching Context: Use
driver.switchTo().window(windowHandle)
to change the WebDriver's context to a specific window or tab. - Robustness: While Thread .sleep() is used here for simplicity, it's better to use WebDriver's explicit waits (e.g., WebDriver Wait) for more reliable automation, as they allow you to wait for specific conditions or elements to be available.
.png)