Perform Keyboard Events
Performing keyboard events in Selenium involves simulating key presses or combinations of key presses on a web element. This can include typing text, pressing special keys (like Enter, Tab, or function keys), or combining keys (like Ctrl+C for copy).
Using the Actions Class for Keyboard Events
The Actions class in Selenium provides methods to simulate keyboard actions. Below are some common methods and their uses:
1. sendKeys(CharSequence keysToSend)Sends a sequence of key strokes to the currently focused element.
2. keyDown(Keys key) and keyUp(Keys key)Simulates pressing down and releasing a key, respectively. Useful for key combinations.
3. build() and perform(): build()ompiles all actions into a single step, and perform() executes them.
Code of Perform Keyboard in Events
package asc;
import org.openqa.selenium.By;
import org.openqa.selenium.Keys;
import org.openqa.selenium.WebElement;
import org.openqa.selenium.chrome.ChromeDriver;
import org.openqa.selenium.interactions.Actions;
import io.github.bonigarcia.wdm.WebDriverManager;
public class KeyBoardEvent {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
WebDriverManager.chromedriver().setup();
ChromeDriver program = new ChromeDriver();
program.get("https://extendsclass.com/text-compare.html");
program.manage().window().maximize();
WebElement selectTextArea = program.findElement(By.xpath("//*[@id=\"dropZone\"]/div[2]/div/div[6]/div[1]/div/div/div/div[5]/div[8]/pre"));
Actions action = new Actions(program);
Thread.sleep(3000);
action.keyDown(selectTextArea, Keys.CONTROL).sendKeys("a").sendKeys("c").build().perform();
WebElement DestinationTextArea = program.findElement(By.xpath("//*[@id=\"dropZone2\"]/div[2]/div/div[6]/div[1]/div/div/div/div[5]/div[8]/pre/span"));
Thread.sleep(3000);
action.keyDown(DestinationTextArea, Keys.CONTROL).sendKeys("a").sendKeys("v").build().perform();
}
}

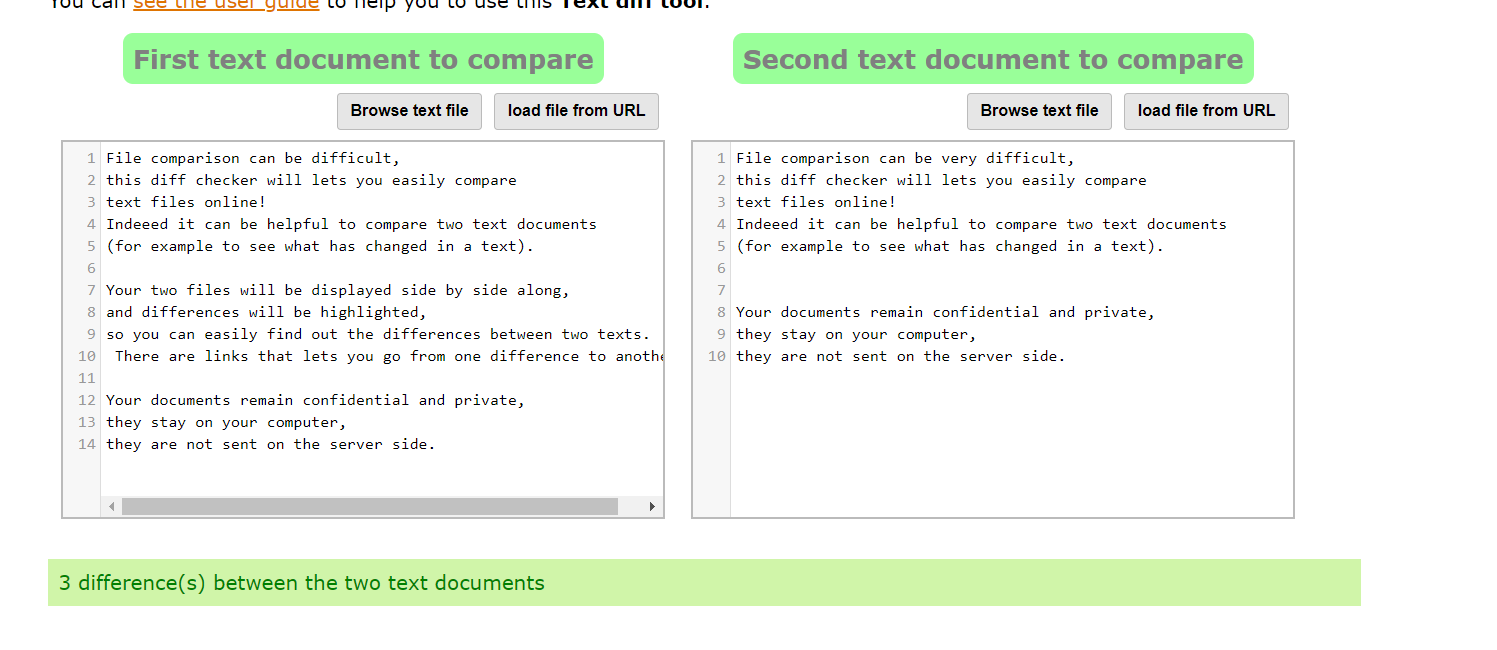
Output

Code Breakdown and Explanation
1. Setup and Initialization:
WebDriverManager.chromedriver().setup();
ChromeDriver program = new ChromeDriver();
WebDriverManager.chromedriver().setup();:
Configures WebDriverManager to automatically download and set up the ChromeDriver.new ChromeDriver();:
Initializes a new instance of the ChromeDriver, which controls the Chrome browser.
2. Navigating to the Web Page:
program.get("https://extendsclass.com/text-compare.html");
program.manage().window().maximize();
program.get("https://extendsclass.com/text-compare.html");:Navigates the browser to a specific URL, which hosts a text comparison tool.program.manage().window().maximize();
Maximizes the browser window to ensure all elements are fully visible and interactable.
3. Locating the Source Text Area:
WebElement selectTextArea = program.findElement(By.xpath("//*[@id=\"dropZone\"]/div[2]/div/div[6]/div[1]/div/div/div/div[5]/div[8]/pre"));
- This line identifies the source text area where the text to be copied is located. The findElement method uses an XPath expression to locate the pre tag within a series of nested div tags. The XPath should be carefully constructed to ensure it points to the correct element on the page.
4. Creating the Actions Object and Performing Copy Action:
Actions action = new Actions(program);
Thread.sleep(3000);
action.keyDown(selectTextArea, Keys.CONTROL).sendKeys("a").sendKeys("c").build().perform();
Actions action = new Actions(program);:
Creates an instance of the Actions class, which is used to build and perform a series of complex user interactions.Thread.sleep(3000);:
Introduces a delay to allow time for the page elements to load completely. It's generally better to use explicit waits rather than Thread .sleep().action.keyDown(selectTextArea, Keys.CONTROL).sendKeys("a").sendKeys("c").build().perform();:Performs a series of keyboard actions:keyDown(selectTextArea, Keys.CONTROL):
Simulates pressing the Control key while focusing on select Text Area.- sendKeys("a"): Simulates pressing 'a' to select all text in the text area.
- sendKeys("c"): Simulates pressing 'c' to copy the selected text to the clipboard.
- build() .perform(): Compiles and executes the sequence of actions.
5. Locating the Destination Text Area and Pasting:
WebElement DestinationTextArea = program.findElement(By.xpath("//*[@id=\"dropZone2\"]/div[2]/div/div[6]/div[1]/div/div/div/div[5]/div[8]/pre/span"));
Thread.sleep(3000);
action.keyDown(DestinationTextArea, Keys.CONTROL).sendKeys("a").sendKeys("v").build().perform();
findElement(By.xpath(...)):
Finds the destination text area where the copied text will be pasted.action.keyDown(DestinationTextArea, Keys.CONTROL).sendKeys("a").sendKeys("v").build().perform();Similar to the copy action, but with sendKeys("v") to paste the clipboard content into the Destination Text Area.
Key Points
Actions Class:
The Actions class is crucial for simulating complex user interactions like keyboard events. The keyDown and sendKeys methods allow for precise control over keyboard actions.Element Focus:
Ensure the target element is properly focused before performing keyboard actions. This is important for text areas or input fields to receive the simulated keystrokes.Using XPaths:
The code relies heavily on XPath expressions to locate elements. These XPaths need to be accurate to avoid issues likeNoSuchElementException
.Synchronization:
The use of Thread .sleep() for delays is not recommended for production code. Explicit waits using Web Driver Wait and Expected Conditions provide better control and efficiency.
.png)